
-
- [adsw_currency_switcher]
- Home
- About Us
- Catalog
- Track Your Order
- Contact Us
- Shipping & Delivery

TSMC closed 2025 with one of the strongest quarters in its history, driven by sustained AI demand, accelerating advanced-node adoption, and disciplined execution. While the earnings presentation highlighted record financial performance and an upbeat outlook, the earnings call transcript revealed deeper strategic signals that are critical for understanding where TSMC’s growth and risks truly lie.
Here are presentation highlights and the earnings call insights to provide a complete picture of TSMC’s trajectory.
Table of Contents
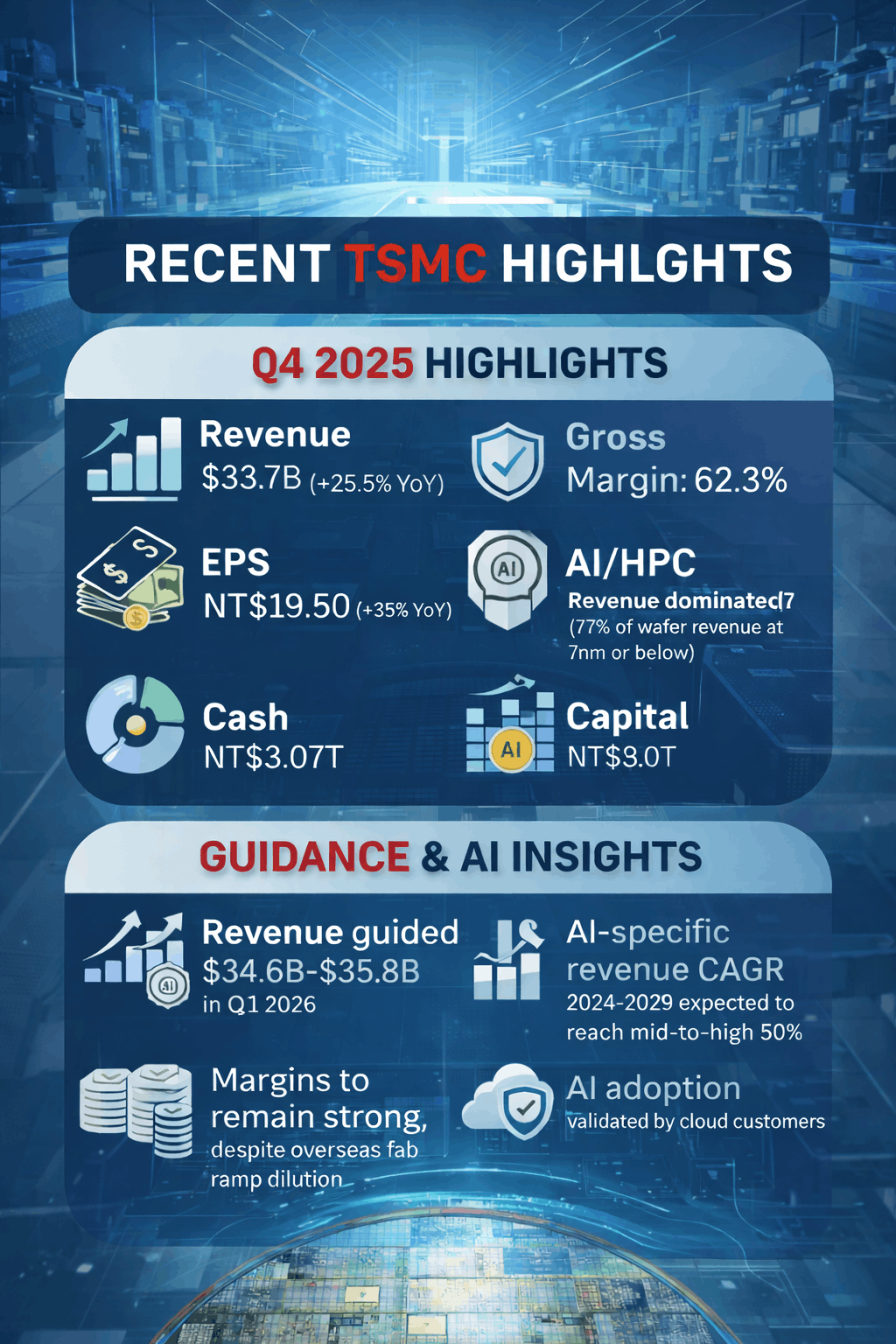
In the fourth quarter of 2025, TSMC reported revenue of US$33.73 billion, exceeding guidance and growing 25.5 percent year over year. In NT dollar terms, revenue reached NT$1.05 trillion, up 20.5 percent year over year. Profitability expanded meaningfully, with gross margin rising to 62.3 percent and operating margin reaching 54.0 percent. Net profit margin climbed to 48.3 percent, reflecting strong utilization and favorable product mix.
Net income attributable to shareholders increased 35 percent year over year to NT$505.7 billion, while diluted earnings per share rose to NT$19.50. These results confirm that TSMC is converting AI-driven demand into real earnings power rather than just top-line growth.
Advanced technologies continued to dominate revenue contribution. In the fourth quarter, 3-nanometer accounted for 28 percent of wafer revenue, 5-nanometer for 35 percent, and 7-nanometer for 14 percent. Overall, 77 percent of wafer revenue came from technologies at 7-nanometer and below, underscoring how central leading-edge nodes have become to TSMC’s business.
By platform, High Performance Computing remained the largest contributor at 55 percent of fourth-quarter revenue, followed by smartphones at 32 percent. On a full-year basis, HPC revenue grew 48 percent year over year and accounted for 58 percent of total 2025 revenue. This confirms that AI workloads, data centers, and advanced compute are no longer incremental drivers but the structural backbone of TSMC’s growth
For the full year 2025, TSMC reported revenue of US$122.4 billion, up 35.9 percent year over year. Gross margin improved to 59.9 percent and operating margin expanded to 50.8 percent. Full-year diluted earnings per share reached NT$66.25, representing 46.4 percent growth compared to 2024.
Operating cash flow reached NT$2.27 trillion, while free cash flow exceeded NT$1 trillion despite record capital expenditures. Cash dividends continued to increase, reinforcing management’s commitment to shareholder returns even during heavy investment cycles.
For the first quarter of 2026, management guided revenue between US$34.6 billion and US$35.8 billion, with gross margin expected between 63 percent and 65 percent and operating margin between 54 percent and 56 percent. Capital expenditures for 2026 are planned at US$52 billion to US$56 billion, signaling continued aggressive investment in leading-edge manufacturing and advanced packaging.
Looking further ahead, management expects 2026 revenue to grow by close to 30 percent in US dollar terms. Over the medium term, revenue CAGR is expected to approach 25 percent, with long-term gross margin sustained at 56 percent or higher and return on equity remaining in the high-20 percent range through the cycle.
Management revealed that the CEO personally spent the last three to four months speaking not only with direct customers, but also with their customers, mainly hyperscale cloud providers. These cloud companies shared concrete financial evidence that AI workloads are already generating real business returns, not experimental spending. This direct validation from end customers was cited as a key reason TSMC is confident in committing to very large capital expenditures. This depth of demand confirmation does not appear in the slides
C.C. Wei disclosed that AI is already being used internally within TSMC fabs to improve productivity. He stated that even a 1 to 2 percent productivity improvement translates into meaningful margin benefit for TSMC and partially explains why gross margin held up despite rising manufacturing costs. This operational AI usage is not discussed in the presentation materials.
The slides showed strong YouTube revenue growth, but the call explained the underlying mechanics. YouTube Shorts now generate more revenue per watch hour than traditional in-stream ads in the US, and Shorts carry a lower revenue share, supporting margin improvement. At the same time, subscriptions such as YouTube Premium and YouTube Music continue to grow, with subscribers generating higher lifetime value than ad-supported users. Management described YouTube as a twin-engine model powered by both ads and subscriptions.
While slides show strong margins, the transcript disclosed that N3 (3nm) gross margin is expected to cross above the corporate average sometime in 2026. This is an important profitability milestone that was not explicitly shown in the slides and signals maturing economics at advanced nodes.
Management quantified margin dilution more precisely in the call. Overseas fab ramp-ups are expected to dilute gross margin by 2 to 3 percent in early stages and 3 to 4 percent in later stages. Additionally, initial 2nm ramp is expected to dilute gross margin by 2 to 3 percent for full-year 2026. The slides only reference margins at a high level without this breakdown.
The transcript revealed that advanced packaging contributed slightly over 10 percent of revenue in 2025 and is expected to grow to low-teens percentage of revenue by 2026, growing faster than the corporate average. This specific revenue contribution was not shown in the presentation charts.
Management disclosed that AI accelerators accounted for a high-teens percentage of total revenue in 2025. More importantly, they raised their five-year AI accelerator revenue CAGR outlook to mid-to-high 50 percent for 2024 to 2029. The slides mention AI growth qualitatively but do not provide this level of numeric specificity.
The transcript confirmed that TSMC has already purchased a second large piece of land in Arizona and is actively preparing permits for a fourth fab and the first advanced packaging fab in the region. It was also stated that yield and defect density in Arizona are now close to Taiwan levels. These execution details were not shown in the slides.
Management stated clearly that even with the US$52 to US$56 billion capital expenditure in 2026, capacity relief will be minimal in 2026 and only partial in 2027. Most supply relief is expected in 2028 to 2029 due to fab construction lead times. This timeline was discussed verbally but not reflected in the presentation
The call clarified that recent wafer ASP increases are largely offsetting inflation in tools, materials, labor, and overseas fab costs. Management emphasized pricing remains strategic rather than opportunistic, and that utilization rate and manufacturing productivity are more important drivers of profitability than pricing alone. This nuance is not visible in the slides.
Contrary to media speculation, management stated that TSMC is reducing some 6-inch and 8-inch capacity but is not abandoning mature-node customers. Capacity adjustments are being made to optimize resources while continuing to support profitable customer demand. This clarification does not appear in the presentation.
Thank you for reading this post. If you enjoy this post, please share it with your friends or family members. Let’s get life transformed together! Many thanks.
Trending Posts

FCT 1Q FY26 Earnings Highlights: Stable Traffic, 99.9% Occupancy and AEI Growth Pipeline


VICOM FY2025 Earnings Highlights: 12 Key Takeaways for Investors


Copart Q2 FY2026 Earnings: 10 Key Takeaways on Insurance Trends, ASP Growth and Buybacks

Alphabet GOOGL Q4 2025 Earnings: 10 Key Takeaways on AI, Cloud Growth and $400B Revenue Milestone
Trending Posts

FCT 1Q FY26 Earnings Highlights: Stable Traffic, 99.9% Occupancy and AEI Growth Pipeline


VICOM FY2025 Earnings Highlights: 12 Key Takeaways for Investors


Copart Q2 FY2026 Earnings: 10 Key Takeaways on Insurance Trends, ASP Growth and Buybacks

Alphabet GOOGL Q4 2025 Earnings: 10 Key Takeaways on AI, Cloud Growth and $400B Revenue Milestone

10 Key AMD Earnings Insights From Q4 2025 and FY 2025 Every Investor Should Know

Amazon Q4 2025 Earnings Deep Dive: 10 Hidden Insights from the Press Release and Transcript

Meta Earnings Q4 2025: 12 Things Investors Miss If They Only Read The Press Release

Apple Q1 2026 Earnings Breakdown: Hidden Call Insights Investors Missed
Copyright 2021 © MR Life Changer | Powered by www.mrlifechanger.com
For business collaboration/enquiries, please contact: mr.life.changer9@gmail.com